Mule MUnit testing with variables and properties
Let's see how we can unit test our flows involving variables and properties.
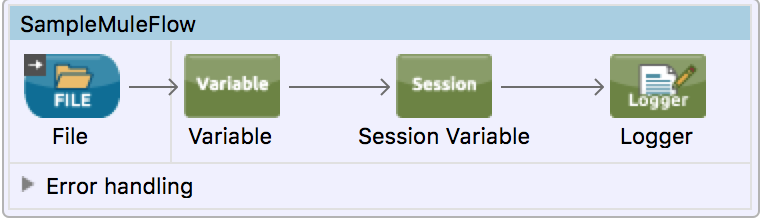
Flow Variables, Session Variables, Inbound/Outbound properties are very common in mule flows. Mule MUnit framework makes it very easy to unit test any Mule Flow and subflows. In this post, we will see how we can unit test our flows involving variables and properties.
Let’s consider a simple mule flow that reads a file and then sets a flow variable and session variable.

<flow name="SampleMuleFlow">
<file:inbound-endpoint path="input" responseTimeout="10000" doc:name="File"/>
<set-variable variableName="fileName" value="#[message.inboundProperties.originalFilename]" doc:name="Variable"/>
<set-session-variable variableName="sessFileName" value="#[flowVars.fileName]" doc:name="Session Variable"/>
<logger message="#[payload]" level="INFO" doc:name="Logger"/>
</flow>
Creating XML MUnit Test Case
If you are using Anypoint Studio, then you can right click our flow, choose MUnit –> Create New Suite. Studio will automatically create an MUnit Test suite under /src/test/munit and adds a test case to it. It should look like –
What we will do here –
- MUnit mocks all inbound connectors and endpoints, so we will need to manually set the test message for the flow. We will do that by adding
<munit:set>component. We will also set an inbound property originalFilename and invocation/flow variable on the message. - Call our main flow with using flow-ref
- After main flow is executed, we will verify that flow variable value is same as what we set on message.
Our final XML Unit Test –
<munit:test name="testmule-test-suite-SampleMuleFlowTest" description="Test">
<munit:set payload="#[getResources('test.txt').asStream()]" doc:name="Set Message">
<munit:invocation-properties>
<munit:invocation-property key="fileName2" value="test2.txt"/>
</munit:invocation-properties>
<munit:inbound-properties>
<munit:inbound-property key="originalFilename" value="test.txt"/>
</munit:inbound-properties>
</munit:set>
<flow-ref name="SampleMuleFlow" doc:name="Flow-ref to SampleMuleFlow"/>
<munit:assert-on-equals expectedValue="#[flowVars.fileName2]" actualValue="#['test2.txt']" doc:name="Assert Equals"/>
</munit:test>
We can then run this as a MUnit Test in studio.
Creating Java MUnit Test Case
For those who prefer writing Java instead of XML, MUnit framework provides fluent java api’s to be used with JUnit. You can create java class by extending FunctionalMunitSuite class.
Below is our java test case –
package testmule;
import java.io.InputStream;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.mule.api.MuleEvent;
import org.mule.api.MuleMessage;
import org.mule.api.transport.PropertyScope;
import org.mule.munit.runner.functional.FunctionalMunitSuite;
public class SampleTestCase extends FunctionalMunitSuite {
@Override
protected String getConfigResources() {
return "testmule2.xml";
}
@Test
public void testSampleFlow(){
InputStream is = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("test.txt");
MuleMessage msg = muleMessageWithPayload(is);
try {
msg.setProperty("originalFileName", "test.txt", PropertyScope.INBOUND);
MuleEvent test = testEvent(msg);
test.setFlowVariable("fileName2", "test2.txt");
MuleEvent reply = runFlow("SampleMuleFlow", test);
Assert.assertEquals("Verify Flow Variable", "test2.txt", reply.getFlowVariable("fileName2"));
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Points to note –
- Create a MuleMessage using
muleMessageWithPayloadfunction provided byFunctionalMunitSuitesuper class. - Creating a MuleEvent using
testEventfunction provided byFunctionalMunitSuitesuper class. - Inbound and Outbound properties can be set on the Message we created. For flow variables and session variables, we will use the test `MuleEvent. testEvent(msg)`` method do not copy flow variables and session variables into test event so setting anything on msg will get lost while creating test event.
- Finally, we call our main flow and verify the value of our flow variable in returned message
So keep testing your code!
More Reading –
Twitter
Google+
Facebook
Reddit
LinkedIn
StumbleUpon
Email